Welcome to our guide on uncovering the mysteries of your Ubuntu system’s configuration! Whether you prefer the simplicity of graphical interfaces or the power of terminal commands, we’ve got you covered. In this comprehensive post, we’ll walk you through exploring your PC’s configuration using both methods—without touching the terminal and with the command line. Let’s dive in!
Exploring PC Configuration without Terminal:
System Settings:
• Click on the “Activities” menu located at the top-left corner of your desktop.
• Type “Settings” and click on the icon to open the System Settings.
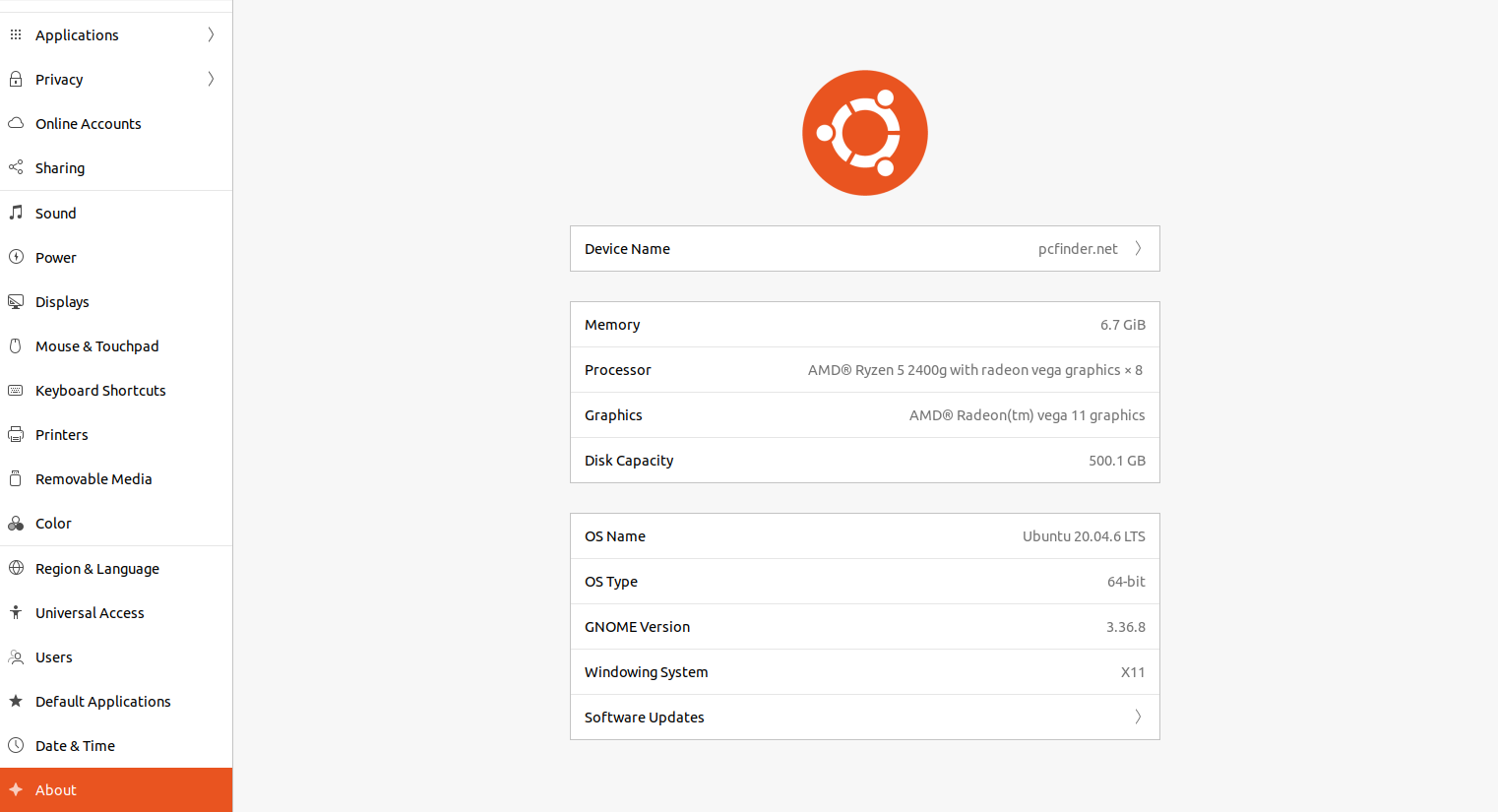
• In the Settings window, select “Details” or “About” depending on your Ubuntu version.
• Here, you’ll find basic information such as the OS version, processor, memory (RAM), and graphics.
• However, this method may not provide detailed hardware specifications.
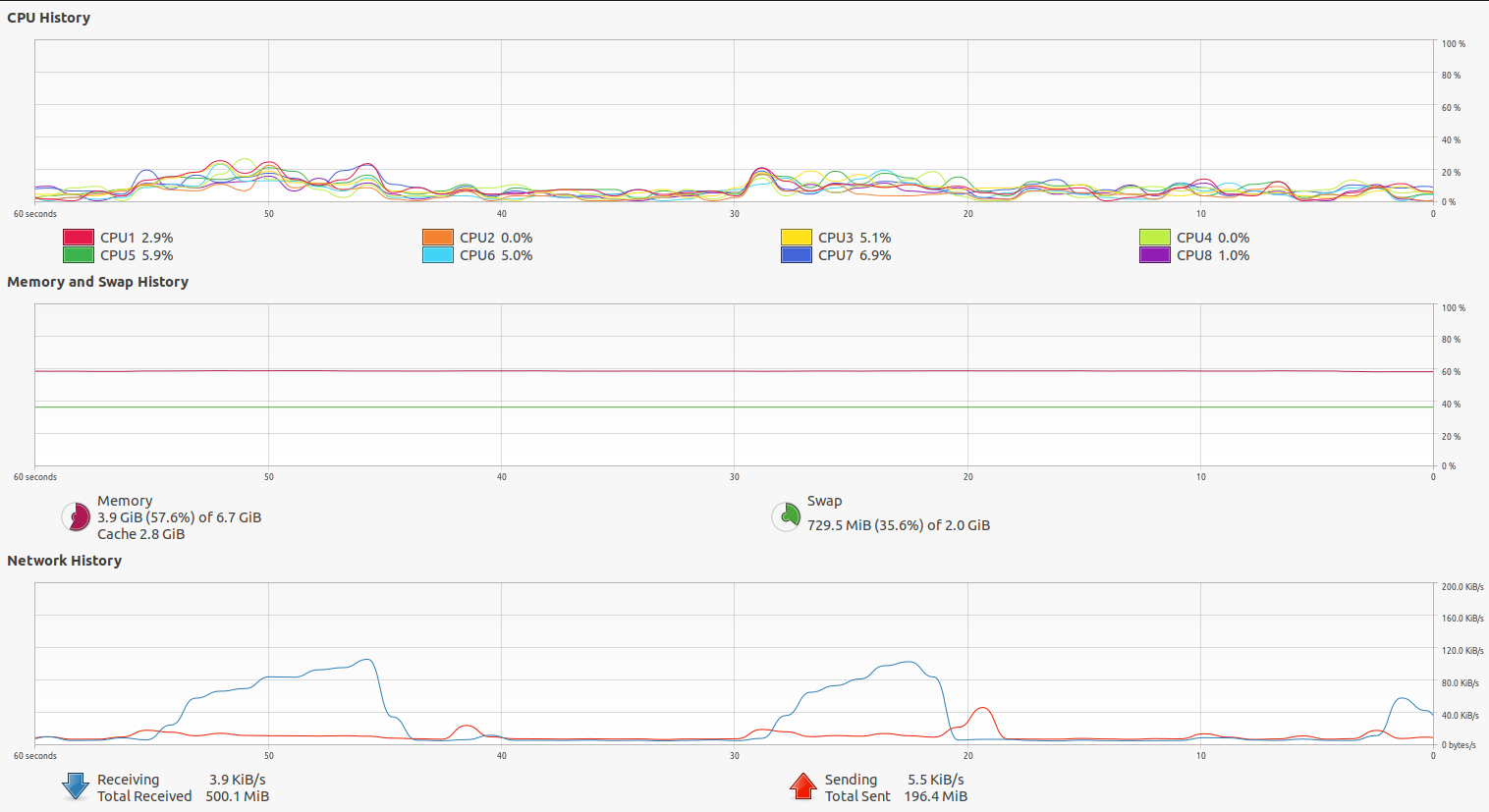
System Monitor:
• To access System Monitor, click the “Activities” button at the top-left corner of your desktop, then type “System Monitor” in the search bar and press Enter.
• It offers real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
Disk Usage Analyzer:
• Click the “Activities” button at the top-left corner of your desktop, then type “Disk Usage Analyzer” in the search bar and press Enter to open it.
• This tool visualizes disk space usage, helping you identify large files and directories efficiently.
Exploring PC Configuration with Terminal:
Terminal commands offer a direct and efficient way to access your system’s configuration. Let’s take a look at some essential commands and what they unveil:CPU Information:
CPU Information: Unveil CPU details like architecture and speed using the lscpu command.
Memory (RAM) Usage: Peek into RAM usage, including free and used memory, with the free -h command.
Disk Usage: Explore disk space, revealing filesystem type and usage, using the df -h command.
Hardware Details: Dive into hardware specifics, from CPU to peripherals, by running sudo lshw -short in the terminal.
Graphics Card Information: Fetch graphics card details effortlessly with the lspci -v | grep -A 12 VGA command.
Network Interfaces: Check network interfaces, IP addresses, and status with the ip addr show command.
Kernel Version: Reveal the currently running kernel version by typing uname -a in the terminal.
Conclusion:
Whether you prefer the efficiency of terminal commands or the simplicity of graphical interfaces, exploring your Ubuntu system’s configuration is a breeze. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can uncover valuable insights into your PC’s hardware and software components with ease. Happy exploring, and may you continue to unveil the potential of your Ubuntu system!